- Reviews
- 1
- Joined
- Dec 16, 2018
- Messages
- 357
- Reaction score
- 556
- Website
- bowkerafricanhunts.com
- Deals & offers
- 25
- Media
- 245
- Articles
- 6
The Gemsbok
The Gemsbok is a large antelope native to the Kalahari, and adapted to live in this hot, dry habitat - a desert specialist. With their long spear like horns and striking coloring species make it a favorite with trophy hunters.
Taxonomy notes:
The name "Gemsbok" in English is derived from Afrikaans Gemsbok, which itself is derived from Dutch name of the male chamois, Gemsbok, Although some superficial similarities in appearance (especially in the facial pattern) are noticed, the chamois and the oryx are not closely related. Previously regarded as a single species, Gemsbok (O. gazella) and Beisa Oryx (O. beisa), from East Africa, are now considered distinct species based on taxonomic results

Fig 1: About the Gemsbok name.
Description:
Gemsbok are light brownish-grey to tan in colour, with lighter patches toward the bottom rear of the rump. Their tails are long and black in colour. A blackish stripe extends from the chin down the lower edge of the neck, through the juncture of the shoulder and leg along the lower flank of each side to the blackish section of the rear leg. They have muscular necks and shoulders, and their legs have white 'socks' with a black patch on the front of both the front legs, and both genders have long, straight horns. They stand about 1.2m at the shoulder. The body length can vary from 190 to 240cm and the tail measures 45 to 90cm. Male Gemsbok can weigh between 180 and 240kg , while females weigh 100–210kg.
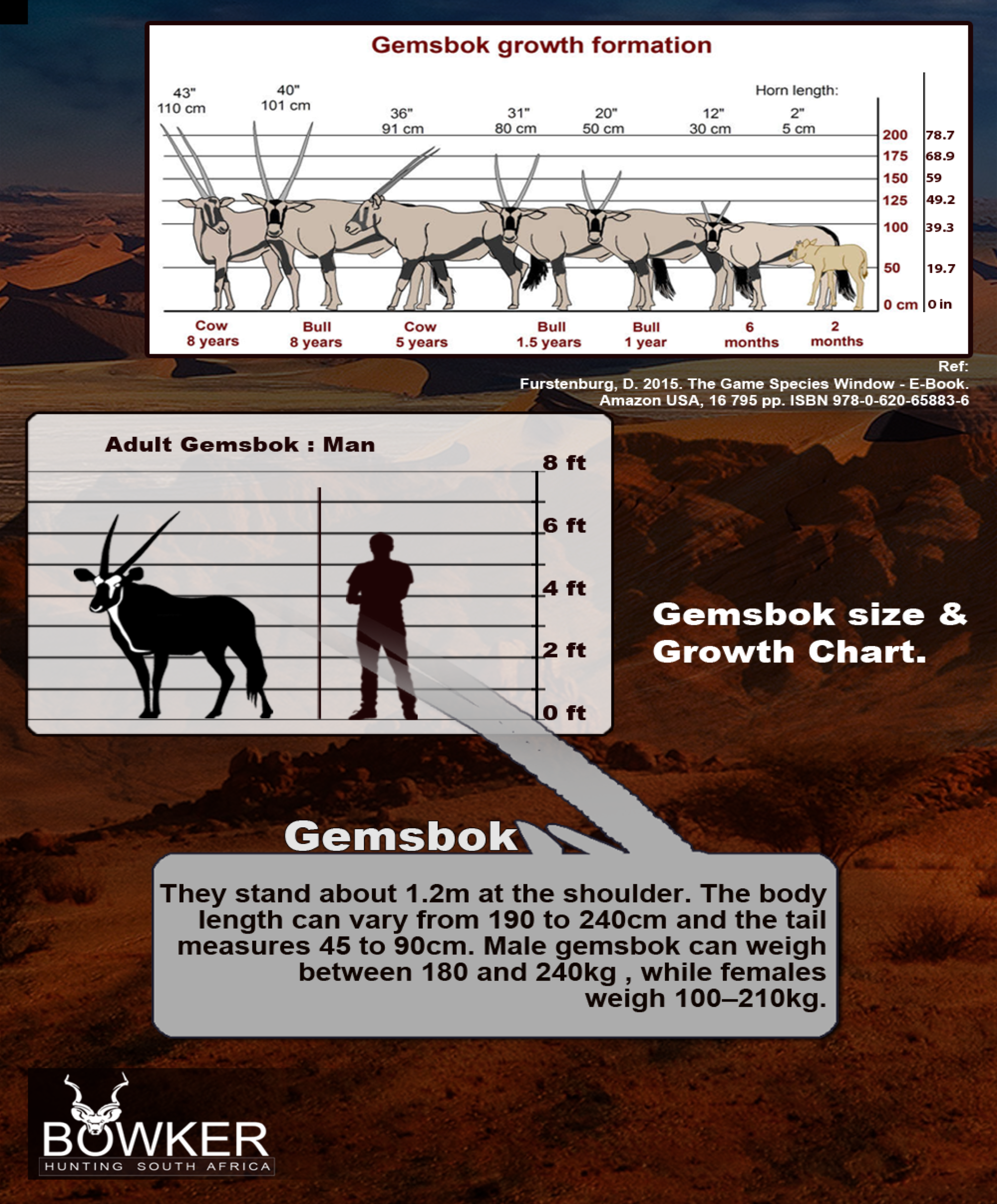
Fig 2: Growth and size charts.
Distribution:
Gemsbok or Oryx were traditionally found in the north-western and western parts of South Africa, which is the Northern Cape, Kalahari, North West and Western Cape.
In the present day, due to commercial game farming and through breeding and selling, they occur throughout South Africa on game farms. There are no Gemsbok in the Kruger National Park, but they can be seen in a number of other parks especially in the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park
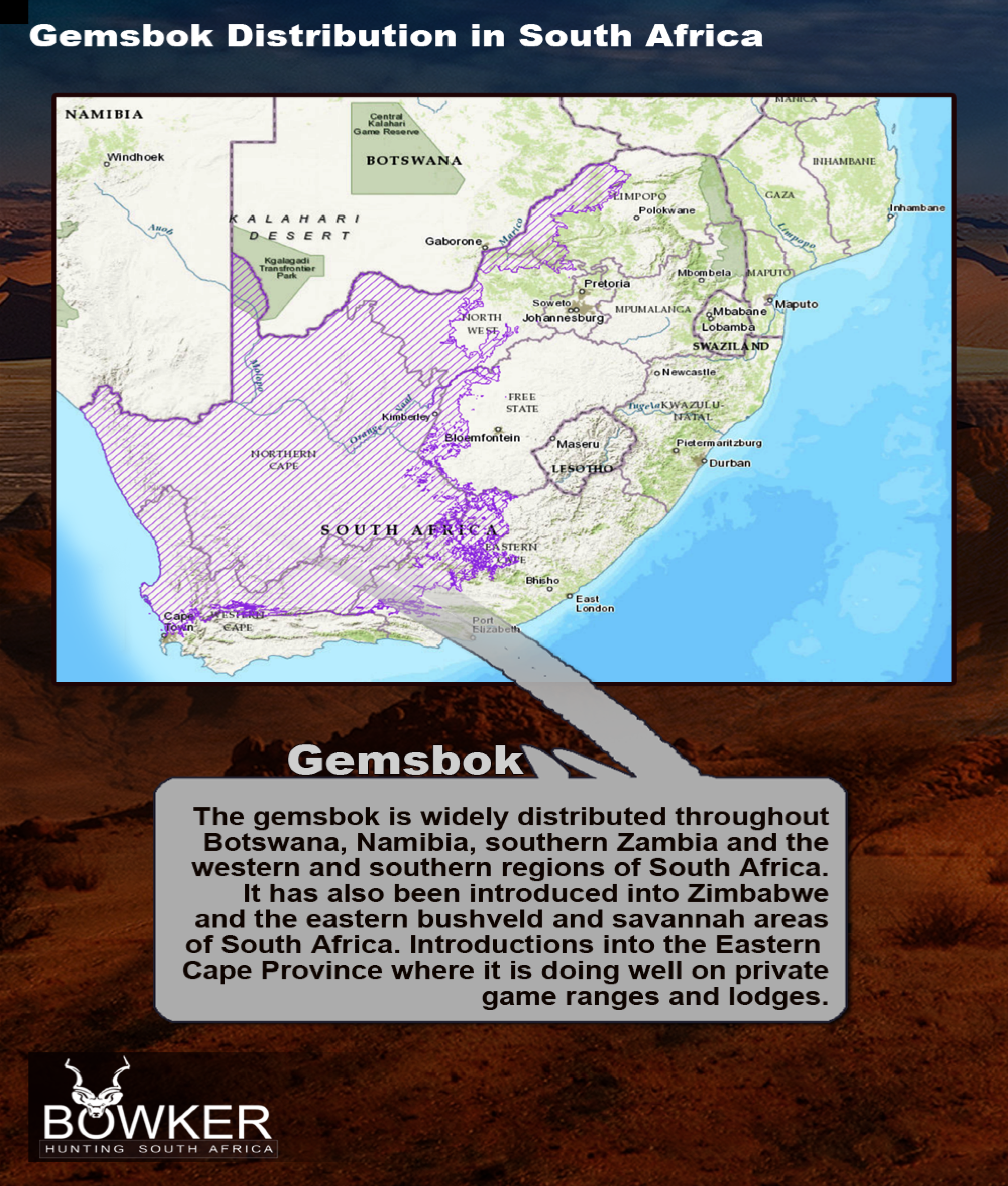
Fig 3: Distribution in South Africa.
Interesting facts:
A low metabolism allows them to survive for much of the year without drinking. They get the moisture they need from their food, including desert melons that they dig up in times of drought. Feeding at night provides them with dew on the leaves with enough water to survive on.They use their horns in territorial combat and as lethal weapons against predators by lowering the horns to a vertical position, even capable of killing lions.

Fig 4: Interesting about the Gemsbok.
Habitats and Ecology:
The Gemsbok is desert dwelling animal that prefers deserts, scrubland and brushland. Southern gemsbok tend to inhabit open, arid areas, such as the Kalahari duneland and bush savannah while northern gemsbok inhabit open grasslands.

Fig 5: Natural Predators.
Behavior:
After the rain season, they usually gather into larger herds of up to 300 individuals. Herds are usually led by a territorial male who marks his territory with piles of dung pellets to warn off male intruders. If intruders do come on to the territory duel conflicts usually occur involving horn clashing and body bashing. As calves in the herd grow, they test each other in what looks like games, but in reality are tests of strength. As the hierarchy becomes established, the need to fight is reduced.

Fig 6: Gemsbok family group.
Types of herds:
They are semi-gregarious and occur in the following groups:
1. mixed groups of 540 individuals that include several territorial bulls as temporarily associates, adult non-lactating cows and sub adult cows
2. family groups of 4-12 animals consisting of adult cows and calves and, sometimes, a territorial bull
3. bachelor herds of 2-7 bulls of all ages
4. solitary territorial bulls.

Fig 7: Different types of herds.
Hunting Gemsbok:
There are various methods of hunting gemsbok in Africa. Generally, there will be a mix of driving, walking and spot and stalk.In an optimal world, a .300 Win. Mag or similar is probably perfect for gemsbok because it is a hard hitting and flat shooting calibre, but a .270 is plenty adequate for gemsbok. Be prepared to shoot out to 350 yards if needed.

Fig 8: Gemsbok shot placement.
The Gemsbok Trophy:
The gold standard for a very nice trophy gemsbok is one with 40 inch horns. Both bulls and cows have horns and are hunted, but a bull gemsbok at 40 inches is much more of a trophy than a female of the same length. The Safari Club International (SCI) scoring method of gemsbok favours length of horns over mass.

Fig 9: The Gemsbok trophy.
Gemsbok males and females make spectacular trophies. Both sexes carry long spear-like horns. Gemsbok can be extremely aggressive and dangerous when injured or threatened. This is one of the most popular antelope to hunt in Southern Africa.

Fig 10: Gemsbok Skull.
References:
Smithers, RHN, 1983. The Mammals of the Southern African Subregion, 1st edn. University of Pretoria, CTP
Book Printers, Cape Town.
Wikipedia.com, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gemsbok
https://www.ewt.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/17.-Gemsbok-Oryx-gazella_LC.pdf
http://www.wildlifesouthafrica.com/blog/mammals-of-south-africa/gemsbok-fact-file
https://animalcorner.org/animals/gemsbok/
Focus on the Gemsbok (Oryx gazella)Deon Furstenburg, GEO WILD Consult (Pty) Ltd.
The Gemsbok is a large antelope native to the Kalahari, and adapted to live in this hot, dry habitat - a desert specialist. With their long spear like horns and striking coloring species make it a favorite with trophy hunters.
Taxonomy notes:
The name "Gemsbok" in English is derived from Afrikaans Gemsbok, which itself is derived from Dutch name of the male chamois, Gemsbok, Although some superficial similarities in appearance (especially in the facial pattern) are noticed, the chamois and the oryx are not closely related. Previously regarded as a single species, Gemsbok (O. gazella) and Beisa Oryx (O. beisa), from East Africa, are now considered distinct species based on taxonomic results
Fig 1: About the Gemsbok name.
Description:
Gemsbok are light brownish-grey to tan in colour, with lighter patches toward the bottom rear of the rump. Their tails are long and black in colour. A blackish stripe extends from the chin down the lower edge of the neck, through the juncture of the shoulder and leg along the lower flank of each side to the blackish section of the rear leg. They have muscular necks and shoulders, and their legs have white 'socks' with a black patch on the front of both the front legs, and both genders have long, straight horns. They stand about 1.2m at the shoulder. The body length can vary from 190 to 240cm and the tail measures 45 to 90cm. Male Gemsbok can weigh between 180 and 240kg , while females weigh 100–210kg.
Fig 2: Growth and size charts.
Distribution:
Gemsbok or Oryx were traditionally found in the north-western and western parts of South Africa, which is the Northern Cape, Kalahari, North West and Western Cape.
In the present day, due to commercial game farming and through breeding and selling, they occur throughout South Africa on game farms. There are no Gemsbok in the Kruger National Park, but they can be seen in a number of other parks especially in the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park
Fig 3: Distribution in South Africa.
Interesting facts:
A low metabolism allows them to survive for much of the year without drinking. They get the moisture they need from their food, including desert melons that they dig up in times of drought. Feeding at night provides them with dew on the leaves with enough water to survive on.They use their horns in territorial combat and as lethal weapons against predators by lowering the horns to a vertical position, even capable of killing lions.
Fig 4: Interesting about the Gemsbok.
Habitats and Ecology:
The Gemsbok is desert dwelling animal that prefers deserts, scrubland and brushland. Southern gemsbok tend to inhabit open, arid areas, such as the Kalahari duneland and bush savannah while northern gemsbok inhabit open grasslands.
Fig 5: Natural Predators.
Behavior:
After the rain season, they usually gather into larger herds of up to 300 individuals. Herds are usually led by a territorial male who marks his territory with piles of dung pellets to warn off male intruders. If intruders do come on to the territory duel conflicts usually occur involving horn clashing and body bashing. As calves in the herd grow, they test each other in what looks like games, but in reality are tests of strength. As the hierarchy becomes established, the need to fight is reduced.
Fig 6: Gemsbok family group.
Types of herds:
They are semi-gregarious and occur in the following groups:
1. mixed groups of 540 individuals that include several territorial bulls as temporarily associates, adult non-lactating cows and sub adult cows
2. family groups of 4-12 animals consisting of adult cows and calves and, sometimes, a territorial bull
3. bachelor herds of 2-7 bulls of all ages
4. solitary territorial bulls.
Fig 7: Different types of herds.
Hunting Gemsbok:
There are various methods of hunting gemsbok in Africa. Generally, there will be a mix of driving, walking and spot and stalk.In an optimal world, a .300 Win. Mag or similar is probably perfect for gemsbok because it is a hard hitting and flat shooting calibre, but a .270 is plenty adequate for gemsbok. Be prepared to shoot out to 350 yards if needed.
Fig 8: Gemsbok shot placement.
The Gemsbok Trophy:
The gold standard for a very nice trophy gemsbok is one with 40 inch horns. Both bulls and cows have horns and are hunted, but a bull gemsbok at 40 inches is much more of a trophy than a female of the same length. The Safari Club International (SCI) scoring method of gemsbok favours length of horns over mass.
Fig 9: The Gemsbok trophy.
Gemsbok males and females make spectacular trophies. Both sexes carry long spear-like horns. Gemsbok can be extremely aggressive and dangerous when injured or threatened. This is one of the most popular antelope to hunt in Southern Africa.
Fig 10: Gemsbok Skull.
References:
Smithers, RHN, 1983. The Mammals of the Southern African Subregion, 1st edn. University of Pretoria, CTP
Book Printers, Cape Town.
Wikipedia.com, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/gemsbok
https://www.ewt.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/17.-Gemsbok-Oryx-gazella_LC.pdf
http://www.wildlifesouthafrica.com/blog/mammals-of-south-africa/gemsbok-fact-file
https://animalcorner.org/animals/gemsbok/
Focus on the Gemsbok (Oryx gazella)Deon Furstenburg, GEO WILD Consult (Pty) Ltd.

